Artificial intelligence (AI) holds tremendous potential to improve our lives and build a better future for the world. Not only can AI automate mundane tasks, but it can also make groundbreaking discoveries such as accelerating the development of new drugs by predicting molecular interactions. Unfortunately, the environment is being impacted by a significant surge in energy consumption needed for the training and operation of AI models and datasets. This translates directly into increased greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, exacerbating the climate crisis. According to OpenAI researchers Dario Amodei and Danny Hernandez, the amount of computing power used for deep learning research has been doubling every 3.4 months since 2012. Projections indicate that by 2040, the information and communications technology (ICT) sector could account for 14% of global emissions, with AI infrastructure—primarily data centers and networks—being the main contributor. These trends underscore the critical need to address AI’s growing carbon footprint and its impact on environmental degradation.
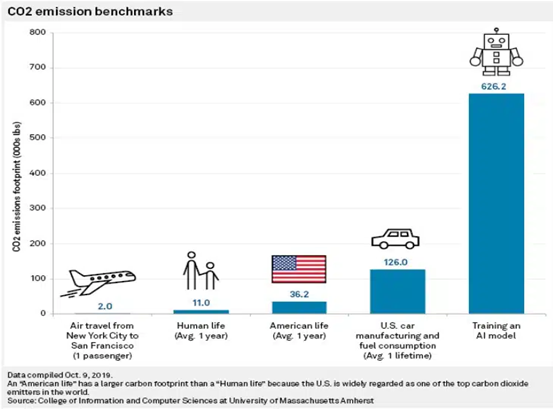
A recent study by University of Massachusetts researchers quantified the energy requirements for training popular large AI models. Their findings revealed that the training process can generate about 626,000 pounds of carbon dioxide emissions. To put this in perspective, it is equivalent to the carbon footprint of roughly 300 round-trip flights between New York and San Francisco, or nearly five times the lifetime emissions of an average car.
As technology and the environment are increasingly connected, the development of sustainable AI and AI for sustainability represent a promising solution to address pressing challenges. Though related, each has distinct objectives. Sustainable AI focuses on developing environmentally friendly AI systems, while AI for sustainability leverages AI technologies to address environmental challenges, focusing on issues like climate change, resource management, and conservation.
Sustainable AI Mitigates Environmental Impacts
In an effort to reduce the carbon footprint of AI systems, sustainable AI emphasizes energy efficiency, data sustainability, and transparency. The goal is to lessen the carbon and ecological footprint of AI systems throughout the entire lifecycle from initial design and production, operational use, and final decommissioning. By adopting sustainable practices, the AI community can help ensure that this powerful technology contributes to a more sustainable future.
Sustainable AI practices include:
- Energy efficiency: More energy-efficient algorithms and hardware reduces the overall energy consumption of AI systems.
- Renewable energy: Renewable energy sources to power data centers and AI training, significantly reducing carbon emissions.
- Hardware optimization: Hardware designed specifically for AI applications to improve energy efficiency and reduce the need for excessive cooling.
- Data center optimization: Implementing energy-efficient cooling systems and optimizing data center operations to minimize environmental impact.
- Responsible sourcing: Hardware components are sourced ethically and sustainably to reduce the environmental footprint of AI systems.
AI for Sustainability for Environmental Solutions
AI for sustainability is the application of AI to address environmental challenges and promote sustainable practices. It involves utilizing AI technologies to analyze data, optimize processes, and make informed decisions that contribute to a more sustainable planet.
Key applications include:
- Climate change: AI can be used for predictive modeling and reducing carbon footprint. Because AI can analyze vast amounts of data, it is able to help us predict climate patterns, extreme weather events, and potential impacts. AI can also optimize energy consumption, transportation routes, and manufacturing processes to minimize carbon emissions.
- Resource management: AI can help monitor water usage, detect leaks, and optimize irrigation systems for water conservation. AI-powered systems can sort waste more efficiently, improve recycling rates, and reduce landfill waste. AI contributes to sustainable agriculture by optimizing crop yields, reducing pesticide use, and improving land management practices.
- Environmental monitoring: Because AI can analyze images and data to monitor wildlife populations and identify threats to biodiversity, it enables biodiversity conservation. AI-powered sensors can detect air, water, and soil pollution, enabling timely intervention.
- Renewable energy: AI can optimize the performance of renewable energy systems like solar and wind farms. AI is also able to manage the integration of renewable energy sources into the electrical grid.
By leveraging AI’s capabilities, we can develop innovative solutions to address pressing environmental challenges and build a more sustainable future.
Companies Leveraging AI Technology for Sustainable Solutions
Google DeepMind: The subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. (Google’s parent company) has used AI to improve energy efficiency in data centers, reducing cooling costs by up to 40%. It has been instrumental in helping Google achieve other sustainability goals by applying Its advanced AI technology to other areas including renewable energy integration, climate modeling and prediction, and sustainable product development:
Tesla: Tesla uses AI to improve the sustainability of its products, operations, and supply chain. AI is used to optimize battery performance, manage energy consumption, streamline manufacturing processes, and improve supply chain efficiency. By leveraging AI, Tesla contributes to a more sustainable future.
IBM: IBM’s AI technology is being used to monitor biodiversity and predict climate change impacts. Sustainability applications include geospatial AI to analyze satellite imagery and other data sources, AI foundation models to improve understanding and response to climate challenges, and AI-powered tools to support sustainability efforts. These technologies enable organizations to make informed decisions and take action to mitigate these challenges.
Ultimately, the future of AI and sustainability depends on how we balance its potential benefits with its environmental costs. By prioritizing sustainable AI development and using AI as a tool for positive environmental change, we can create a more sustainable and equitable future. Bottom line, the environmental footprint may depend more on how we use the technology, and these choices may contribute to or alleviate the effects of climate change.


