In 2023, the global beer market was valued at approximately $1.1 trillion, and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 6.5% between 2024 and 2030. The growth is likely due to the increasing penetration of e-commerce, continued technological innovation, and increasing demand. Current trends in the market include the manufacturing of non-alcoholic beer, new products with natural additives and coloring agents, more use of e-commerce platforms, using artificial intelligence (AI) to make higher quality beer, and even the new trend of immunity-boosting beer. In addition, there is an increasing popularity of craft beer and the emergence of more independent breweries.
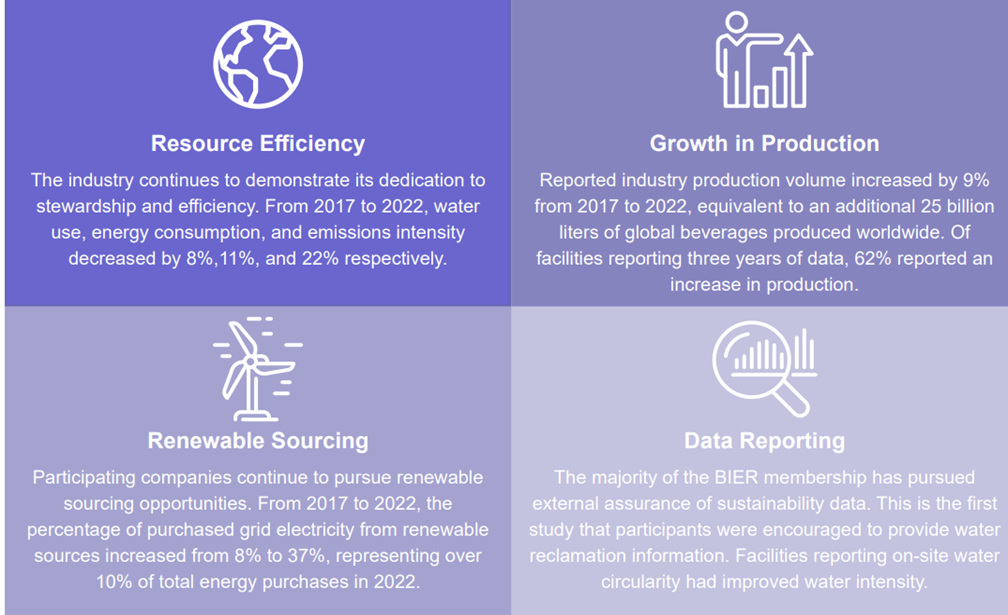
The Beverage Industry Environmental Roundtable (BIER) in 2023 conducted a benchmarking study that included facility-level data for 2017, 2020, and 2022 from 14 BIER members and two partners that showed improvements in water, energy, and emissions intensity ratios by 8%, 11%, and 22% respectively. In addition, continued progress is being made through a variety of facility categories, production volumes, and geographic locations – showcasing that the beverage industry continues to improve business performance while proactively reducing environmental impacts worldwide.
Climate Change and the Beer Industry
Climate change poses a significant threat to the beer industry. With rising temperatures and changing weather patterns, the quality and availability of key ingredients like hops and barley is beginning to be negatively impacted. Warmer conditions lead to reduced yields and altered flavors, while increased pests and diseases can further damage crops. In addition, brewing requires substantial amounts of water, and drought conditions can deplete water supplies. This can lead to higher production costs and potential beer shortages.
To adapt to these challenges, the beer industry is taking proactive measures. Research and development (R&D) efforts are focused on developing new hop and barley varieties that are more resilient to climate change, as well as exploring innovative brewing techniques to reduce water usage. Sustainable practices, such as water conservation measures in breweries and supporting sustainable agriculture for hop and barley production, are also being implemented. It is important that brewers, farmers, scientists, and policymakers collaborate to address these climate-related challenges.
The impact of climate change on the beer industry extends beyond production costs and availability. It can also affect the variety of beer styles available, as changes in hop yields and quality may limit the range of flavors and aromas. In addition, consumer awareness of climate change’s impact on beer can drive demand for sustainable practices and encourage support for environmentally friendly brewing initiatives. The beer industry contributes to climate change in several ways.
- Water Usage: Barley, a key ingredient in beer, requires a significant amount of water resulting in breweries using large amounts of water in the brewing process.
- Energy consumption: The brewing process involves energy-intensive steps like malting, mashing, boiling, and cooling. Often this energy comes from fossil fuel sources, which contributes to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- Transportation: Because beer needs to be transported, often by trucks, from breweries to distribution centers and then to stores, this results in GHG emissions.
- Packaging: Because beer is often packaged in materials like glass bottles, aluminum cans, and cardboard boxes, the production and transportation of these materials contribute to emissions.
- Ingredient supply chain: The supply chain for ingredients like barley and hops often involves long-distance transportation and energy-intensive farming practices, adding to the industry’s carbon footprint.
The beer industry is beginning to recognize that key components of beer, barley and hops, are particularly vulnerable to the changing climate. Warmer temperatures and more frequent droughts are affecting the yield and quality of barley crops. In particular, hops, the aromatic flower that gives beer its distinctive bitterness and flavor, are facing challenges. A rising temperature leads to earlier ripening, reducing the alpha acid content that provides bitterness and aroma. In addition, traditional brewing processes are energy intensive, and the industry’s reliance on water for irrigation and production adds to its environmental footprint.
There are some companies in the beer industry that are taking steps to adopt sustainable agriculture practices. They are looking at a combination of using drought-resistant crop varieties, implementing efficient irrigation techniques, and minimizing the use of harmful chemicals. In addition, breweries are implementing water recycling systems to minimize water usage and reduce wastewater discharge. These advanced water treatment technologies help reduce pollution and improve water quality.
The beer industry is examining how the packaging of beer can play a role in reducing environmental impact. Many breweries are shifting toward lightweight, recyclable packaging materials like aluminum cans and glass bottles. Reducing the amount of packaging material used and optimizing transportation routes can further minimize the industry’s carbon footprint. While some breweries are taking steps to reduce their environmental impact, the overall beer industry remains a significant contributor to climate change.
Case Studies
Carlsberg is a global brewing company known for its commitment to sustainability. Carlsberg aims to achieve zero carbon emissions from its breweries by 2030. The company is investing in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels. The company is developing innovative packaging solutions, such as the world’s first paper bottle made from sustainably sourced wood fibers. This approach reduces the use of plastic and glass, minimizing waste. Carlsberg is committed to responsible water usage, implementing water-saving technologies and practices across its operations. In addition, the company is working towards sourcing all its grains from regenerative farming practices by 2040. This helps improve soil health, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration.
Heineken is another major global brewing company with a strong commitment to sustainability. Across its full beer portfolio, Heineken’s target is that 100% of its barley and hops globally come from renewable, sustainable sources by 2030. By 2021, it was 65% of the way toward achieving that goal. Heineken aims to reduce its carbon footprint significantly and transition to renewable energy sources. The company is working toward net-zero carbon emissions across its value chain. Heineken is committed to reducing waste and promoting circular practices, such as recycling and reuse of materials. Heineken is also working with suppliers to promote sustainable agricultural practices, such as reducing pesticide use and conserving water. And finally, the company is focused on sourcing ingredients locally to reduce transportation emissions and support local economies.
Conclusion and Recommendations
The global beer market, valued at approximately $1.1 trillion in 2023, is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by factors like e-commerce, technological advancements, and increasing populations. However, the industry’s environmental impact is a growing concern. To address these challenges, the beer industry is taking steps towards sustainability including adopting sustainable agriculture practices, implementing water recycling systems, and using eco-friendly packaging materials.
Some companies, like Carlsberg and Heineken, are leading the way in sustainability efforts. Carlsberg aims for zero carbon emissions by 2030, invests in renewable energy, develops sustainable packaging solutions, and promotes responsible water usage. Heineken targets 100% sustainable sourcing of barley and hops, reduces its carbon footprint, promotes circular economy practices, and supports sustainable agriculture.
By accelerating sustainable agriculture, investing in renewable energy, optimizing water usage, promoting sustainable packaging, supporting research and innovation, collaborating with suppliers and consumers, and learning from successful case studies, the beer industry can contribute to a more sustainable future while ensuring the long-term viability of its products.


