In the US alone, 38% of all food goes unsold or uneaten, creating a $444 billion opportunity for the nation, including $250 billion for food companies alone. Food waste contributes 6% to national greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and consumes more than 20% of the US freshwater supply, while, at the same time, one in eight Americans face food insecurity. Recently, a major initiative to cut food waste received support when Starbucks announced it was joining Walmart, Sodexo, and others as a member. With more than 15,000 US stores, Starbucks is the largest quick-service restaurant (QSR) to sign up for the US Food Waste Pact. Other members include Ahold Delhaize USA, ALDI US, Amazon Fresh, Aramark, Bob’s Red Mill, Chick-fil-A, Compass Group USA, Health Care Without Harm, ISS Guckenheimer, Lamb Weston, R&DE Stanford Food Institute, Raley’s, and Whole Foods Market.
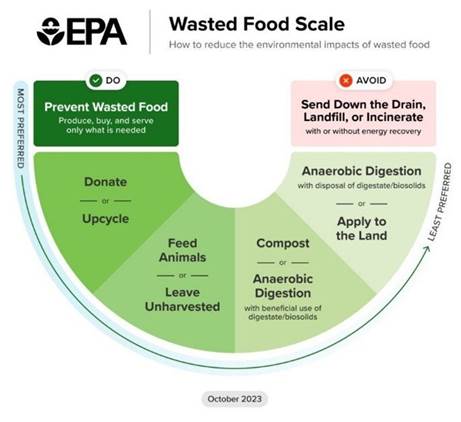
The US Food Waste Pact is a valuable initiative that helps drive progress toward the national goal of reducing food waste by 50% by 2030. It is a collaborative effort between food companies, nonprofit organizations, and government agencies designed to help food companies accelerate their progress toward waste reduction targets by providing them with resources and support.
Key Features of the US Food Waste Pact
- Aligned around the global framework of “Target, Measure, Act,” which encourages companies to set ambitious waste reduction targets, measure their progress, and take action to reduce waste.
- Facilitates precompetitive collaboration among food companies, which provides them with the opportunity to share best practices and find solutions to common challenges.
- Emphasizes the importance of data-driven decision-making, providing companies with the tools and resources to track waste and identify areas for improvement.
- Offers resources and support to help companies reduce waste, including technical assistance, training, and access to best practices.
Starbucks
Starbucks, an American multinational chain of coffeehouses and roastery reserves, is focused on reducing food waste, primarily through its innovative FoodShare program. Launched in 2016, FoodShare focuses on donating unsold, safe food to those in need, operating in 100% of company-owned stores in the US and Canada as it partners with organizations like Feeding America to distribute surplus food to local food banks and food pantries. Through FoodShare, Starbucks employees collect leftover food at the end of each day, which is then picked up by refrigerated trucks and transported to distribution centers, where it is sorted and delivered to local food banks and pantries. This ensures that surplus food reaches those facing hunger, preventing it from ending up in landfills.
Since 2016, Starbucks’ FoodShare program has diverted over 75 million pounds of food from waste streams, which is equivalent to more than 63 million meals, while also investing over $81.5 million in hunger relief efforts, demonstrating its dedication to both environmental sustainability and community support. The company has set a goal to reduce food waste by 50% in its US operations with a target of 2030.
Walmart
Walmart, a leading global American retailer, is actively engaged in reducing food waste through a multi-faceted approach, which includes its key focus on prevention achieved through improved inventory management and close collaboration with suppliers to optimize ordering and ensure produce quality. When prevention is not possible, the company focuses on repurposing and donating excess food. This includes donating unsold but safe items to local food banks and charities, providing nourishment to those in need, and repurposing Items not suitable for sale, such as making croutons from day-old bread or using rotisserie chicken in prepared meals.
Recycling and composting are also part of Walmart’s food waste reduction efforts, achieved through partnerships. For example, the company’s partnership with Denali facilitates the efficient transformation of non-edible food waste into valuable resources, which are then used for composting, animal feed, and even the generation of renewable energy.
Technology also plays a crucial role in improving Walmart’s processes, with innovations like the Zero DePack system to automate the separation of food waste from packaging, which makes the recycling process more efficient and reduces contamination. This technological advancement streamlines waste management and maximizes resource recovery.
Whole Foods
Whole Foods Market, an American multinational supermarket, is committed to reducing food waste through a variety of initiatives, focusing on prevention and donation, aiming to cut food waste in half by 2030, mirroring the EPA’s Food Recovery Hierarchy. The company works with its suppliers to utilize “imperfect” produce in prepared foods and its juice and smoothie bars, preventing it from going to waste at the source. Whole Foods also creatively repurpose ingredients within its stores, such as using leftover fish in seafood soups or damaged produce in prepared dishes and baked goods.
Through partnerships with organizations like Food Donation Connection, Whole Foods donates millions of pounds of safe perishable and non-perishable food annually to local food banks and food rescue agencies. Its “Nourishing Our Neighborhoods” program further supports this effort by donating refrigerated vans to community-based food rescue programs, facilitating the transport of rescued food to those in need.
Whole Foods also focuses on diversion, with many stores participating in programs designed to keep food waste out of landfills, including composting, anaerobic digestion, and animal feed programs. The company also utilizes innovative technologies like the Grind2Energy system, which converts food waste into renewable energy through anaerobic digestion. Whole Foods actively tracks its progress and works with waste haulers to ensure proper diversion of food waste, continually assessing emerging technologies, and partnering with experts to improve its landfill diversion rates. By combining these various strategies, the company demonstrates a comprehensive approach to minimizing food waste and contributing to a more sustainable food system.
Conclusion
The concerted efforts of industry leaders like Starbucks, Walmart, and Whole Foods, as demonstrated through their participation in the US Food Waste Pact and implementation of innovative programs like FoodShare, optimized inventory management, and creative repurposing techniques, signify a pivotal shift toward a more sustainable and equitable food system. These companies’ commitment to the “Target, Measure, Act” framework, coupled with collaborative partnerships and technological advancements, not only address the staggering economic and environmental costs of food waste but also directly combat food insecurity. By setting ambitious reduction goals and actively diverting surplus food from landfills, these companies are leading the charge in achieving the national objective of halving food waste by 2030, proving that collaborative, data-driven strategies can create meaningful and lasting change.


